Johannes Diderik van der Waals, a Dutch physicist, is celebrated for his groundbreaking contributions to thermodynamics and molecular physics. His work has revolutionized our understanding of the behavior of gases and liquids and laid the foundation for many modern scientific advancements. Known primarily for the Ban der Waals equation and forces, his legacy endures in fields ranging from physical chemistry to material science. This article explores his life, discoveries, and the lasting impact of his work on the scientific community.

Early Life and Education
Johannes Diderik van der Waals was born on November 23, 1837, in Leiden, Netherlands. He grew up modestly as the son of a carpenter, yet his curiosity and passion for learning were evident from an early age. Despite financial constraints, Van der Waals pursued education with vigor, eventually becoming a schoolteacher.
Due to the restrictive academic qualifications of the era, he lacked a formal university degree at the time. However, with the Dutch government's reforms in education, Van der Waals obtained a degree from the University of Leiden in 1862, demonstrating exceptional aptitude in mathematics and physics. His academic journey set the stage for the groundbreaking research that would later define his career.
The Van der Waals Equation
One of Van der Waals’ most significant contributions to physics was formulating the van der Waals equation of state in 1873. This equation modifies the ideal gas law to account for the finite size of molecules and the intermolecular forces between them.
The ideal gas law, expressed as PV = nRT, assumes that gases comprise point particles with no volume or interaction. However, this assumption breaks down at high pressures and low temperatures. Van der Waals introduced two corrections to the equation:
• Molecular Volume: Molecules occupy physical space, reducing the free volume available for movement.
• Attractive Forces: Intermolecular forces cause molecules to attract one another, reducing the pressure exerted on the container.
The modified equation:
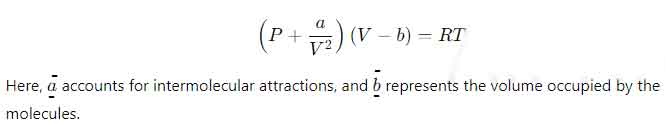
This equation marked a paradigm shift in understanding real gases, bridging the gap between idealized models and observable behavior.
Van der Waals Forces
Another cornerstone of Van der Waals' legacy is his identification of intermolecular forces, which came to be known as Van der Waals forces. These weak forces are responsible for interactions between neutral molecules and play a crucial role in various natural phenomena and technological applications.
Van der Waals forces can be categorized as:
• London Dispersion Forces: Temporary dipoles induced in atoms and molecules.
• Dipole-Dipole Interactions: Forces between polar molecules with permanent dipoles.
• Hydrogen Bonds: A specific, stronger dipole interaction involving hydrogen atoms.
These forces are essential for understanding molecular cohesion, phase transitions, and the behavior of materials at the nanoscale.
Nobel Prize in Physics
Van der Waals’ contributions were formally recognized in 1910 when he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics. The Nobel Committee honored him for his work on the equation of state for gases and liquids, highlighting its profound implications for physical chemistry and thermodynamics.
This recognition underscored the universal applicability of his findings, influencing studies on fluids, polymers, and colloids. It also affirmed his position as one of the most influential physicists of his time.
Legacy in Science
Van der Waals’ work has had a lasting impact on multiple scientific disciplines:
• Chemistry: His theories are fundamental to understanding solutions, mixtures, and chemical reactions in non-ideal conditions.
• Physics: The van der Waals equation remains critical in thermodynamics and statistical mechanics.
• Material Science: Van der Waals forces explain properties of layered materials like graphene and the adhesion of surfaces.
• Biology: These forces influence protein folding, DNA interactions, and the behavior of cell membranes.
Personal Life and Character
Johannes Diderik van der Waals was known for his humility and dedication to science. Despite his challenges in pursuing higher education, his perseverance and intellectual curiosity allowed him to overcome barriers. His modest beginnings did not deter him from making contributions that would shape the future of science.
Van der Waals was deeply committed to his family and teaching, balancing his professional work with personal responsibilities. This balance of intellect and humility made him a respected figure among his peers and students.
Exploring the Life and Legacy of André Gide A Pioneer in Modern Literature
While Van der Waals’ achievements lie in science, his life shares similarities with that of other trailblazers in different fields, such as André Gide. Gide, a pioneer in modern literature, used his works to challenge conventional norms and explore human authenticity. Similarly, van der Waals questioned traditional assumptions in physics and developed theories that pushed the boundaries of human understanding. Both figures demonstrate how dedication to one’s craft can lead to transformative societal contributions.
Relevance in Modern Research
Van der Waals’ discoveries remain relevant in contemporary research. His theories underpin advancements in nanotechnology, where intermolecular forces are crucial for designing molecular machines and materials.
For example, in the Van der Waals heterostructures study, researchers stack atomically thin layers of materials like graphene to create devices with unique electronic properties. These applications highlight the enduring significance of his work in cutting-edge science.
Moreover, Van der Waals’ insights are integral to developing computational models in chemistry and physics. Modern simulations of molecular systems often incorporate his principles to achieve accurate predictions.
Educational Influence
Van der Waals’ legacy also extends to education. His work is a staple in physics and chemistry curricula, inspiring generations of students to explore the intricate behavior of matter. The simplicity and elegance of his equations make them an essential tool for understanding complex systems.
His story reminds us that perseverance and curiosity can lead to groundbreaking discoveries, even in adversity.
Conclusion
Johannes Diderik van der Waals was a visionary whose contributions to physics and molecular science continue to influence today's world. From the van der Waals equation to the discovery of intermolecular forces, his work provided a deeper understanding of the physical world and laid the groundwork for countless advancements in science and technology.
Van der Waals exemplified the power of human curiosity and innovation through his dedication and intellect. His legacy inspires us, reminding us of science's transformative potential in understanding and shaping our world.